LTV helps a marketer find out how much money customers bring to a business, plan expenses on advertising campaigns more accurately, and evaluate their payback. We will tell you how to calculate the LTV indicator and what to do to improve it.
What is LTV and why is it important to calculate it?
What data is needed to calculate LTV
LTV calculation formulas
How to increase LTV
Expert advice
Read Also:How Good Is ChatGPT Really and How Can It Make Marketers’ Jobs Easier?
What is LTV and why is it important to calculate it?
Table of Contents
LTV (from English lifetime esteem) may be a metric that makes a difference you get it whether showcasing costs pay off and assess the effectiveness of a commerce show. For case, a Web advertiser sets up publicizing campaigns, and it is important for him to get it which ones work well and which ones don’t .
Let’s say a master went through 100,000 ₽ on publicizing in a month, and the company’s income for the same period was 50,000 ₽. It appears that everything is awful and the commerce is unrewarding, but clients can come back and purchase more. The LTV pointer makes a difference to see how much cash clients bring in over a certain period of time.
It happens that pulling in a customer costs 1000 ₽, and within the to begin with month he brings as it were 100 ₽, that’s , he covers as it were 10% of the costs. At that point the same client proceeds to purchase and in a year brings in a add up to of 2000 ₽. This implies that the costs of attracting one client have paid off and brought benefit.
As a rule, LTV is an normal marker. Depending on the circumstance, ready to conversation around the LTV of a particular client or a gather of users. For example, housewife Maria brought the company 30,000 ₽ amid the complete time she utilized the wellness app, and a bunch of clients who came to this benefit from VKontakte promoting for Moscow bring 1 million ₽ per year.
What to calculate depends on the errand the marketer wants to fathom. In case you wish to arrange a advancement and send uncommon offers to clients, it is vital to know the LTV of each client to distinguish the more “valuable”. In case you wish to oversee an promoting campaign and turn on/off standards, you would like to assess the LTV of the user group that comes from these standards.
Why Calculate LTV
LTV in marketing helps business owners and marketers determine how effectively they manage the company’s resources and, if necessary, adjust the budget and expenses. For example, to attract one client, a marketer spends 1,000 ₽, and the client brings in a profit of 1 million ₽. This profit can be taken from the company’s turnover, or it can be reinvested and increased investments in advertising to attract even more buyers.
Students of the Internet Marketer course learn to calculate LTV and other metrics using real projects in order to evaluate the effectiveness of advertising and help the company earn more.
What data is needed to calculate LTV
To calculate LTV, a marketer needs at least the following metrics:
● The average revenue
a company receives from a customer over a given period, such as a week, month, or year.
● Cost of attracting a new customer
, or CAC (from English customer acquisition cost) – costs of advertising, marketing and other expenses that help attract buyers.
● The average time
a user remains a customer of the company, in weeks, months or years.
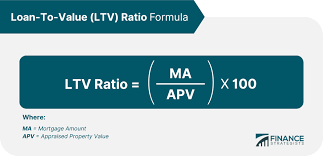
LTV calculation formulas
There are diverse ways to calculate LTV. The choice of strategy depends on the commerce range, the information that the advertiser has, and the objectives of the investigation. For case, to calculate the LTV of one client for a certain period, it is sufficient to essentially include up all of his installments for this time. For illustration, a individual buys coffee in a web store each month and spends from 2,000 to 5,000 ₽ on each arrange. Let’s calculate his LTV for the year utilizing the equation:
LTV = 2000 + 3500 + 4700 + … + 2900 + 5000 = 36,200 ₽
In regions where the precise “lifetime” of a client in a company is known, another LTV formula can be utilized. For case, clients of an internet school of outside dialects study for an normal of 10 months. The company’s profit from each understudy per month is 3,000 ₽. To discover out the LTV, you wish to duplicate the benefit by the period of use of the item:
LTV = 3000 ₽ x 10 months = 30,000 ₽
You’ll calculate the LTV of a cohort, i.e. a bunch of individuals with comparative characteristics who performed an activity on a certain day or hour. For case, 100 individuals enrolled on the location in a day and made orders for 15,000 ₽. We discover out the LTV of this cohort utilizing the equation:
LTV = 15,000 rubles / 100 = 150 ₽
This strategy makes a difference to assess which promoting campaigns worked more viably, or to distinguish periods of decrease and buyer movement.
Read Also:How to Manage Marketing as an Entrepreneur
How to increase LTV
The LTV indicator is also the total revenue from a client, that is, “increasing LTV” means “earning more”. This can be done in several ways:
● Increase the average check
When customers buy more products at one time, their LTV increases. To do this, they are offered additional products or services.
● Increase customer loyalty
If customers understand that the company takes into account their wishes and requests, they can become regular customers. Customer loyalty can be increased in tangible or intangible ways.
Material methods are special programs, such as cashbacks, cumulative discounts, bonuses. Intangible methods are improving the quality of service, working with negative customer reviews .
● Increase the frequency of purchases
The more purchases a customer makes over a certain period, the higher their LTV, and therefore the company’s profit. You can increase the frequency of purchases using mailings with special offers or personal discounts, gamification and other techniques.
Increasing LTV and business profit is the task of the entire company. Each department or specialist at their level is responsible for ensuring that the product generates income. For example, sales managers communicate politely with customers and do not impose goods or services. Customer support specialists quickly respond to user requests. Cleaning staff maintain cleanliness in the sales area so that customers enjoy being there and want to come back.