There are different ways to work with a company’s clients: setting up advertising for months and holding big promotions, or testing many hypotheses and choosing the ones that work.
What is growth marketing and why is it needed?
How growth marketing differs from traditional marketing
What are growth teams and what types are there?
How to Build a Growth Team
How to test hypotheses and analyze results
Expert advice
What is growth marketing and why is it needed?
Table of Contents
Development promoting is an approach to pulling in and holding clients that’s based on consistent experimentation and speculation testing.
For case, a group is working on a versatile app. Marketers believe that setting up automatic email campaigns to onboard new users will make them more active. And the number of people who buy a subscription in the first days of using the app will increase. The team tests this hypothesis, and if it works, they implement the tool.
The more hypotheses you can test, the higher the chances of finding working ones and increasing the company’s profits.
Growth marketing is usually used by companies that want to achieve rapid and multiple growth: subscribers, customers, revenue. At the same time, it is important to increase other metrics: customer retention, cost reduction.
Read Also:Crafting Success – Your Ultimate Startup Roadmap Creation Guide
How growth marketing differs from traditional marketing
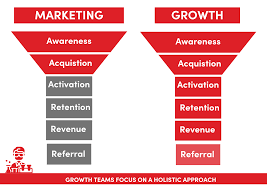
Every business has a sales funnel , which usually consists of 5-6 levels. It is usually called an AAARRR funnel – by the first letters of the level names. In traditional marketing, they often focus on informing and attracting, and the rest work “as it happens”. A growth marketer is responsible for the entire funnel, so their actions bring more results: a person becomes a client, then a regular customer, and then a brand advocate, and this brings even more clients.
In addition to the AAARRR funnel, growth marketing uses “growth loops“. This is a strategy in which the result – in money or other units – at the lower level of the funnel is usually higher than what was invested at the upper level. For example, a team invests 1,000 ₽ in advertising and receives a profit of 1,500 ₽. It puts all this money into advertising and receives 3,000 ₽ in profit: this is how the cumulative effect appears and the growth loop is twisted.
Here’s how growth loops work to attract and retain users: A fitness app offers a customer to invite friends in exchange for additional features or a free month. The customer becomes even more loyal and brings in new users, who in turn attract their friends.
Here’s another difference between traditional and growth marketing.
In traditional marketing:
1.● create large-scale advertising campaigns and then optimize them;
2.● pay more attention to the top of the funnel;
3.● focus on product features.
In growth marketing:
1.● conduct short experiments, scale up successful ones;
2.● work at all levels of the funnel;
3.● take into account the values and needs of the client in order to create or change the product and build a funnel around them – work closely with product teams.
To choose the right strategy for promoting a company on the market, you need to understand the directions of marketing and be able to use different tools. You can learn this on your own or in courses, under the guidance of experienced mentors-practitioners and on real projects.
What are growth teams and what types are there?
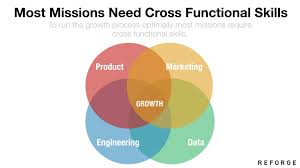
The growth team is responsible for all levels of the funnel, from displaying ads when money is spent to the moment of purchase — when the company receives income. For the team to be effective, it must be cross-functional, i.e. consist of different specialists, such as a marketer, analyst, developer, and designer. The growth department can be functional, but most likely it will include members from different teams.
How to Build a Growth Team
It often happens that the company’s management decides that growth marketing needs to be implemented and distributes the responsibilities of finding and testing hypotheses among employees. But in reality, this approach doesn’t work: the marketer, developer, and designer are primarily engaged in the main work, and there is no time left for experiments.
A growth team can be built in two stages:
1. Determine the growth driver
It is good when the company’s managers already know what the product is growing due to. For example, it could be the work of the sales department, the high virality of the product itself – its distribution by users, or growth due to a loyal customer community. When the growth driver is known, the company hires a growth marketer – the team’s lead.
2. Assemble a team
If the driver is the community, it is desirable that the growth marketer has more experience in building a community than in sales. And if the product grows through sales, you need a specialist in this area. The growth marketer is responsible for which hypotheses to test and which tools to use for this.
A designer who will test creatives for advertising, icons and screenshots for app stores, landing pages, must understand marketing. Because usually product or brand designers do not like to work with marketing tasks.
Team members can work in-house — within the company — or outsourced. For example, a copywriter can start outsourcing and then join the team because his services are needed by several growth marketers, and it is easier to build work processes in a team.
Read Also:Crafting Success – Entrepreneurial Blueprint for Growth
How to test hypotheses and analyze results
There are different methods for testing hypotheses and building a growth strategy in marketing. Let’s look at the HADI framework as an example.
1. H — Hypothesis
first, the marketer builds a hypothesis and defines the metrics that should change. For example, a team of a mobile application for programmers plans to increase the conversion to download. Marketers put forward a hypothesis: if the background color of screenshots in the app store is changed to a darker one, the conversion will increase, because such a color scheme is associated with programming.
2. A — Actions
according to the hypothesis, changes are made to the product and testing is launched. First, the designer prepares new screenshots with a dark background. Then the experiment is launched and screenshots with a dark background are posted on Google Play. The test version is shown to 50% of the audience.
3. D — Data
at this stage, the data of the experiment is collected and analyzed and the metric determined in the first step is assessed to have changed. During the experiment, it turned out that the number of new app installations among the audience that saw the test screenshots was 6.2% higher than in the other group. In such an experiment, this difference has statistical significance, which means the test was successful.
4. I — Insights
at the conclusion stage, they determine whether the hypothesis worked and what to do next. If the hypothesis is confirmed, changes are implemented in the product. If not, the HADI framework is launched again.
The experiment showed that screenshots with a dark background increase conversion to app downloads. It can be concluded that dark looks more attractive to potential users and the new audience finds this color more familiar to products related to programming. The increase in conversion can also be explained by the higher contrast of dark screenshots on the light background of the app store. This helped the illustrations stand out among other programs and attract the attention of users.
The results of the experiment can become the basis for other visual changes, such as icons and video previews of the app in the store, which will increase conversion to downloads.
You can test anything: changes to the appearance of the app in the app store, landing pages on the website, creatives in email, from the subject and preheader of the letter to gifs or memes inside it.
For experiments, you can use a standard template, which consists of three parts.