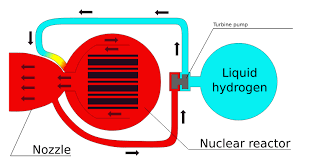
Hydrogen turbines are developing as a promising innovation competent of changing the worldwide vitality scene. This sort of turbine, which employments hydrogen as fuel to produce electrical vitality, speaks to an imaginative arrangement to the challenges of climate alter and the developing request for clean and renewable vitality sources.
Not at all like fossil fills, hydrogen offers clean combustion , discharging as it were water as a byproduct, making it a key player within the move to a low-carbon economy.
Read Also:Advertising on Yandex Maps: how it works, how much it costs and what to consider in campaigns
What is a hydrogen turbine?
Table of Contents
A hydrogen turbine could be a gadget that changes over the chemical energy of hydrogen into mechanical vitality and after that into electrical vitality through a generator. It works on the rule of hydrogen combustion with oxygen to deliver water vapor at tall weight and temperature, which at that point drives the turbine edges, hence producing power. This prepare is characterized by its capacity to create vitality with negligible emanations, with water vapor being the as it were coordinate byproduct, speaking to a clean and maintainable vitality choice compared to fossil fuel-based vitality sources.
The thought of using hydrogen as an vitality source isn’t modern, but its application in turbines for power era has picked up force in later decades , driven by the critical ought to discover maintainable options to fossil powers. The advancement of hydrogen turbines can be followed from early tests and speculations on hydrogen combustion to the improvement of progressed advances that empower its proficient and large-scale utilize.
In the early stages
the center was more on fundamental inquire about and understanding the properties of hydrogen, counting its potential tall vitality effectiveness and the challenges related with its dealing with and combustion. As gas turbine innovation advanced, so did the intrigued in adjusting these machines to utilize hydrogen as a fuel. Specialized challenges, such as hydrogen’s tall burning rate, its wide combustibility extend, and the tall temperatures come to amid combustion, required developments in turbine plan and control frameworks.
Significant advances began to materialise in the 21st century
when the thrust to diminish nursery gas emanations and move forward vitality maintainability got to be a worldwide basic. Inquire about and advancement escalates, centering on making strides the productivity of hydrogen turbines, overseeing NOx (nitrogen oxides) emanations and adjusting existing foundation for hydrogen utilize. Pilot ventures and commercial shows started to appear the practicality of this innovation, not as it were in terms of natural execution but too in terms of its integration into the power lattice and its capacity to supply a dependable and adaptable source of vitality .
Today
hydrogen turbines are at the cutting edge of the vitality move, profiting from developments in green hydrogen generation (hydrogen created from renewable sources) and propels in capacity and dissemination advances. As the innovation proceeds to develop and economies of scale start to diminish costs, hydrogen turbines are anticipated to play an progressively significant part within the worldwide exertion to attain a feasible, low-carbon vitality future.
How a hydrogen turbine works
Its operation, whereas sharing fundamental standards with conventional normal gas turbines, is recognized by interesting characteristics related with the utilize of hydrogen as a fuel . Underneath, we investigate the working standards, key components, and crucial contrasts with normal gas turbines.
As I said some time recently, a hydrogen turbine works on the rule of changing over the chemical vitality of hydrogen into mechanical vitality and after that into electrical vitality. This handle starts with the blend of hydrogen and oxygen (as a rule from the discuss), which is presented into the combustion chamber of the turbine. When touched off, this combustible blend discharges a large sum of vitality within the frame of warm, quickly extending the gasses which at that point stream through the turbine edges at tall speed, driving it to pivot. This rotational movement is exchanged to a generator, which changes over the mechanical vitality into power.
In this tweet from the FLEX4H2 project we have an animation that helps to understand it:
1750081011076006264
These are the key components of a hydrogen turbine
Combustion chamber:
Usually where hydrogen is blended with oxygen and burned to produce tall temperature and weight gasses.
Turbine edges:
Planned to capture the vitality of the extending hot gasses, driving the turbine to turn.
Generator:
Coupled to the turbine, it changes over mechanical vitality into electrical vitality.
Control framework:
Controls the fuel and discuss blend, turbine speed, and power era to optimize operational proficiency and security.
Assistant frameworks:
These incorporate cooling, grease and filtration frameworks, fundamental for the support and operational effectiveness of the turbine.
Read Also:How to Start a Blog from Scratch: Step-by-Step Guide
The FLEX4H2 project
The image in this article is from the FLEX4H2 project
a extend that speaks to an imaginative and key activity outlined to progress hydrogen turbine innovation, underlining the commitment of the European Union and Switzerland to the vitality move towards cleaner and more economical sources. This venture looks for to create and illustrate the reasonability of a gas turbine that can work proficiently with 100% hydrogen, checking a breakthrough on the way towards the decarbonization of large-scale control era.
The most objective of the FLEX4H2 venture is to illustrate that gas turbines can work adaptably with a hydrogen mix of up to 100%, in this way giving a reasonable and feasible vitality arrangement that can be coordinates into existing framework. This venture looks for to overcome the specialized challenges related with hydrogen combustion, counting overseeing tall temperatures and combustion rates, as well as limiting hurtful outflows such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) as said over.
To achieve its ambitious objectives, the FLEX4H2 project involves a number of key stages, including:
Innovative advancement:
Moving forward gas turbine components, such as the combustion chamber, to suit the interesting properties of hydrogen and guarantee proficient and secure operation.
Testing and approval:
Conducting broad testing with diverse hydrogen mixes to survey turbine execution, proficiency and emanations, altering frameworks to optimize operation.
Full-scale show:
Execution of the innovation in a genuine operational environment to illustrate its possibility, adaptability and natural benefits, stamping a significant step towards commercialization.
Within this project we have the GT36 turbine
an innovation from Ansaldo Energia of Italy that has been put into operation in Germany running exclusively on 100% hydrogen. This turbine belongs to the H class, distinguished by its sophistication and ability to achieve operating efficiency and extraordinarily high temperatures.
Capable of generating more than 560 MW of power
the GT36 has the capacity to supply vitality to around 500,000 homes. Usually accomplished much appreciated to the plan of its combustion chamber, which coordinating two complementary frameworks to reach tall working temperatures, whereas keeping emissions to a least without the have to be utilize diluents.
This turbine has too demonstrated competent of consistently transitioning from normal gas to green hydrogen
demonstrating operational versatility crucial to the energy transition and representing a significant step forward in Europe’s efforts to combat climate change.
Until now
the turbines installed by Ansaldo could operate with a mixture containing up to 40% hydrogen. With funding of 8.7 million euros, the FLEX4H2 project aims, in the next three years, to complete the development of a technology that completely dispenses with hydrocarbons and operates solely with hydrogen .